The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Emotional Memory Suppression
Sleep is essential for cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall health. Recent research has shed light on how sleep deprivation can impair the brain’s ability to suppress negative memories, leading to increased emotional distress and potential mental health issues.
Understanding Emotional Memory Suppression
Emotional memory suppression is the brain’s mechanism for controlling intrusive negative thoughts. This process involves the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (rDLPFC), responsible for executive functions like decision-making and emotional regulation, and the hippocampus, which manages memory formation and retrieval. A well-functioning rDLPFC can suppress unwanted memories by modulating hippocampal activity.
The Study: Sleep Deprivation and Memory Control
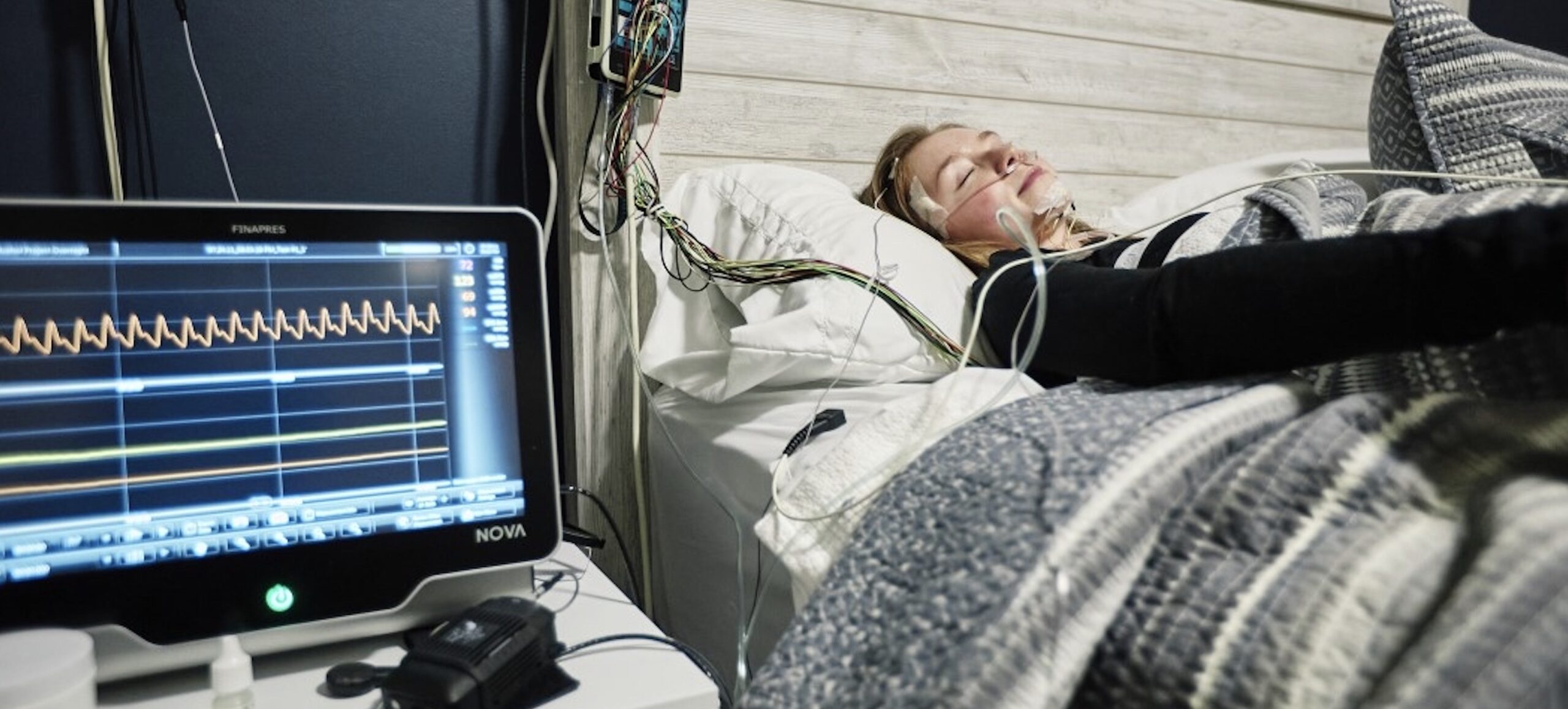
A study conducted by researchers from the University of York and the University of East Anglia explored the effects of sleep deprivation on emotional memory suppression. Eighty-five healthy adults participated, with half receiving a full night’s sleep and the other half staying awake all night. Participants were shown neutral faces paired with negative images (e.g., car crashes) and later asked to either recall or suppress the associated images while undergoing brain activity monitoring.
Key Findings
• Reduced rDLPFC Activity: Sleep-deprived individuals exhibited decreased activity in the rDLPFC during attempts to suppress negative memories, indicating diminished executive control.
• Increased Hippocampal Activity: There was heightened activity in the hippocampus among sleep-deprived participants, suggesting that the brain struggled to inhibit memory retrieval.
• Impaired Memory Suppression: Those lacking sleep had difficulty suppressing negative memories, leading to more frequent intrusive thoughts.
Implications for Mental Health
With a significant portion of adults experiencing sleep issues and mental health challenges, understanding the link between sleep and emotional regulation is crucial. The study’s findings suggest that sleep deprivation hampers the brain’s ability to control negative memories, potentially exacerbating conditions like anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Recommendations for Improving Sleep and Emotional Health
1. Prioritize Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, create a restful environment, and limit exposure to screens before bedtime to enhance sleep quality.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): Consider CBT-I techniques to address sleep disturbances and improve sleep patterns.
3. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate practices such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises to reduce stress and promote better sleep.
4. Limit Stimulant Intake: Avoid caffeine and other stimulants, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, to prevent sleep disruptions.
5. Seek Professional Help: If experiencing persistent sleep problems or emotional distress, consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment options.
Product Recommendations:
To support better sleep and enhance emotional well-being, consider the following products:
Weighted Blanket
Provides deep pressure stimulation to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality.
Memory Foam Pillow
Offers optimal neck support to reduce discomfort and enhance sleep posture.
White Noise Machine
Creates a soothing auditory environment to mask disruptive noises and facilitate restful sleep.
Aromatherapy Diffuser
Utilizes calming essential oils like lavender to create a tranquil sleep atmosphere.
Sleep Eye Mask
Blocks out light to help maintain darkness, encouraging the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Prioritizing sleep is essential for maintaining emotional health and cognitive function. By understanding the impact of sleep deprivation on the brain’s ability to suppress negative memories, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their sleep habits and overall well-being.